
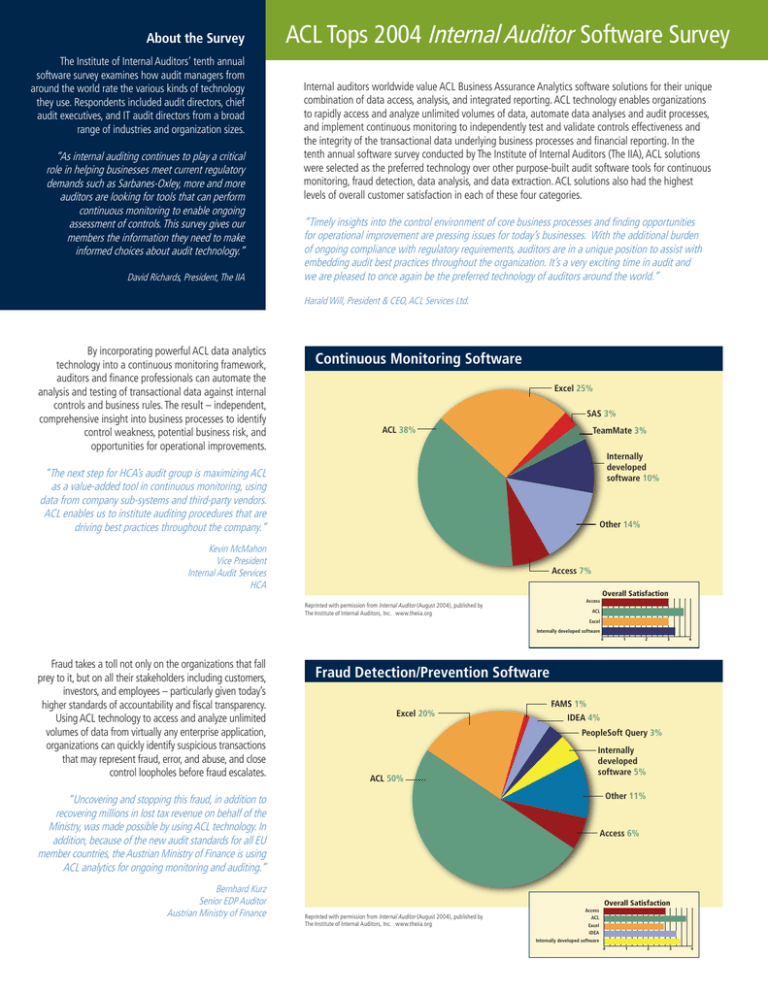
Upon adoption, FASB ASU 2016-14, Not-for-Profit Entities (Topic 958): Presentation of Financial Statements of Not-for-Profit Entities, requires all NFPs to present their expenses by both function and nature in one place, which can be on the face of the Statement of Activities, in a separate statement (such as an SFE), or in the notes to the financial statements. Do I need to include a Statement of Functional Expenses (SFE) in my report? Based on the new guidance, it is possible certain transactions (for example, grants from federal and state governments) that were previously classified as exchange transactions could be classified as contributions after implementation.Īccess more NFP revenue recognition resources here.Īccess more NFP grants and contracts resources here.Ĥ. It also provides clarification on the differentiation between conditional and unconditional contributions. This guidance specifies how an entity can determine whether a transaction is an exchange transaction or contribution. Additionally, there is new guidance for revenue recognition of contributions. Unless those contracts are within the scope of other standards (such as for leases, financial instruments, or insurance contracts), the impact of the new rules must be considered. The guidance affects all entities-public, private, and NFP-that enter into contracts with customers to transfer goods or services or enter into contracts to transfer nonfinancial assets.
The new revenue recognition model replaces virtually all existing revenue recognition guidance. How will the new revenue recognition standard affect NFPs? Net asset classification changed with annual financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after Decemas a result of the issuance of FASB ASU 2016-14, Not-for-Profit Entities (Topic 958): Presentation of Financial Statements of Not-for-Profit Entities. Others are temporary, for example, stipulating that resources be used only after a specified date, for particular programs or services, or to acquire buildings and equipment. Some donor-imposed restrictions impose limits that are permanent, for example, stipulating that resources be held in perpetuity (not used up) or held in an endowment. Importantly, NFPs use recordkeeping systems to monitor and track resources based on donor-imposed restrictions. Net assets are classified based on the existence or absence of donor restrictions. How are net assets classified and recorded? Management’s documentation of its assessments and conclusions is key. Although accounting results may vary based on facts and circumstances, NFPs can improve consistency and accuracy by focusing on key valuation considerations. The short answer is “yes.” The definition of fair value in FASB Accounting Standards Codification® (ASC) 820, Fair Value Measurement, is “the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.” That definition is currently applicable to contributions received by NFPs, including gifts-in-kind (GIK), and leads charities to use fair value, not the most conservative value. Are NFPs required to use fair value for gifts-in-kind? As with most any industry, there are certain aspects of not-for-profit accounting that tend to draw frequent questions. NFP staff and donors rely on financial information to monitor the organization’s adherence to budgets, laws, and regulations, as well as to ensure the successful stewardship of its resources.

For not-for-profit entities (NFPs), accurate financial reporting means more than keeping the auditors and creditors happy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
